
Maximize Your CBSE/RBSE/NCERT Class 10 Science Score: The Ultimate Questions and Answer Guide for Exam Success!

NCERT Class 10 Science Practice Test Paper
Total Marks: 80
Instructions:
- Answer all questions.
- Read each question carefully before answering.
- Write your answers neatly and legibly.
Section A: Objective (1 mark each, total 15 marks)
- The element found in chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants, is:
- A) Calcium
- B) Magnesium
- C) Iron
- D) Carbon
- The force acting between unlike magnetic poles is:
- A) Attractive only
- B) Repulsive only
- C) Neutral
- D) Attracting and repelling depending on distance
- The process of separating a mixture of immiscible liquids based on their different densities is called:
- A) Filtration
- B) Sedimentation
- C) Decantation
- D) Chromatography
- The process by which plants lose water vapor through tiny pores in their leaves is called:
- A) Photosynthesis
- B) Transpiration
- C) Respiration
- D) Guttation
- The SI unit of electric charge is:
- A) Ampere
- B) Volt
- C) Coulomb
- D) Watt
- The type of cell division responsible for producing sex cells (sperm and eggs) is:
- A) Mitosis
- B) Meiosis
- C) Binary fission
- D) Budding
- The process of converting sound waves into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain is called:
- A) Resonance
- B) Hearing
- C) Echolocation
- D) Transduction
- The main component of natural gas, a fossil fuel, is:
- A) Methane
- B) Propane
- C) Butane
- D) Gasoline
- The process of transferring heat energy through direct contact between objects is called:
- A) Conduction
- B) Convection
- C) Radiation
- D) Insolation
- The organ in the human body responsible for filtering waste products from the blood is:
- A) Lungs
- B) Kidneys
- C) Liver
- D) Stomach
- The process of releasing energy from glucose in the presence of oxygen is called:
- A) Photosynthesis
- B) Cellular respiration
- C) Fermentation
- D) Chemiluminescence
- The process of generating electricity using moving magnets and coils of wire is called:
- A) Electromagnetism
- B) Electromagnetic induction
- C) Electrostatic attraction
- D) Photovoltaic effect
- The harmful component of cigarette smoke that damages the lungs and increases the risk of cancer is:
- A) Nicotine
- B) Tar
- C) Carbon monoxide
- D) Oxygen
- The process of separating a mixture of substances based on their different boiling points is called:
- A) Filtration
- B) Centrifugation
- C) Chromatography
- D) Distillation
- The process of converting electrical energy into light energy is called:
- A) Luminescence
- B) Incandescence
- C) Photosynthesis
- D) Electrolysis
Section B: Fill in the Blanks (1 mark each, total 7 marks)
- The chemical formula for baking soda is NaHCO₃.
- The process of releasing energy from food in the absence of oxygen is called anaerobic respiration.
- The SI unit of luminous intensity is the candela (cd).
- The part of the eye that focuses light onto the retina is the lens.
- The type of energy stored in a compressed spring is potential energy.
- The harmful pollutant released by incomplete combustion of fuels is carbon monoxide.
- The process of converting atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia for fertilizers is called the Haber-Bosch process.
Section C: Very Short Answer (1 mark each, total 10 marks)
- Briefly differentiate between metals and non-metals.
- Write the chemical formula for water.
- What is the function of chlorophyll in plants?
- How is sound produced by our voice?
- What is the difference between AC and DC current?
- Briefly explain the water cycle.
- How can we reduce air pollution?
- What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
- What are the symptoms of malaria?
- Briefly explain the process of digestion in humans.
Section D: Short Answer (2 marks each, total 12 marks)
- Draw a labeled diagram of the human heart and briefly explain its function.
- What are the different types of lenses? Briefly explain their properties and uses.
- Describe the working principle of a hydroelectric power plant.
- Explain the concept of acids and bases. Give examples of each.
- What are the benefits and risks of using genetically modified organisms (GMOs)?
- Discuss the importance of biodiversity for maintaining a healthy ecosystem.
Section E: Long Answer (3 marks each, total 9 marks)
- Explain the process of photosynthesis in plants. What are the raw materials and products involved?
- Describe the structure and function of the human nervous system.
- Briefly explain the laws of motion proposed by Isaac Newton. Give examples of each law in action.
Section F: Essay Type (4 marks each, total 12 marks)
- Discuss the impact of human activities on climate change. What are some possible solutions to mitigate its effects?
- Write an essay on the importance of renewable energy sources for a sustainable future.
- Describe the scientific method and its role in developing new knowledge and understanding.
Answers for the multiple-choice questions in Section A as follows:
- (D) Carbon
- (D) Attracting and repelling depending on distance
- (C) Decantation
- (B) Transpiration
- (C) Coulomb
- (B) Meiosis
- (D) Transduction
- (A) Methane
- (A) Conduction
- (B) Kidneys
- (B) Cellular respiration
- (B) Electromagnetic induction
- (B) Tar
- (D) Distillation
- (B) Incandescence
Section B: Fill in the Blanks (Write the missing word)
- NaHCO₃ (Chemical formula for baking soda)
- Anaerobic respiration (Process of releasing energy from food without oxygen)
- Candela (cd) (SI unit of luminous intensity)
- Lens (Part of the eye that focuses light onto the retina)
- Potential energy (Type of energy stored in a compressed spring)
- Carbon monoxide (Harmful pollutant released by incomplete combustion)
- Haber-Bosch process (Process for converting atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia)
Section C: Very Short Answer (Write a concise answer)
- Metals are good conductors, malleable, and ductile, while non-metals are poor conductors, brittle, and often have unique chemical properties.
- H₂O (Chemical formula for water)
- Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and plays a crucial role in photosynthesis.
- Vibrations of the vocal cords in the larynx create sound waves.
- AC current changes direction periodically, while DC current flows in one constant direction.
- The water cycle involves water evaporating, rising, condensing, and falling back to Earth as precipitation.
- Reducing car emissions, using public transportation, and conserving energy are some ways to reduce air pollution.
- Decomposers break down dead organisms and return nutrients to the soil, allowing new plants to grow.
- Fever, chills, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches are some symptoms of malaria.
- Food is broken down by enzymes in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Nutrients are absorbed, and waste products are eliminated in digestion.
Section D: Short Answer (2 marks each, total 12 marks)
1. Human Heart:
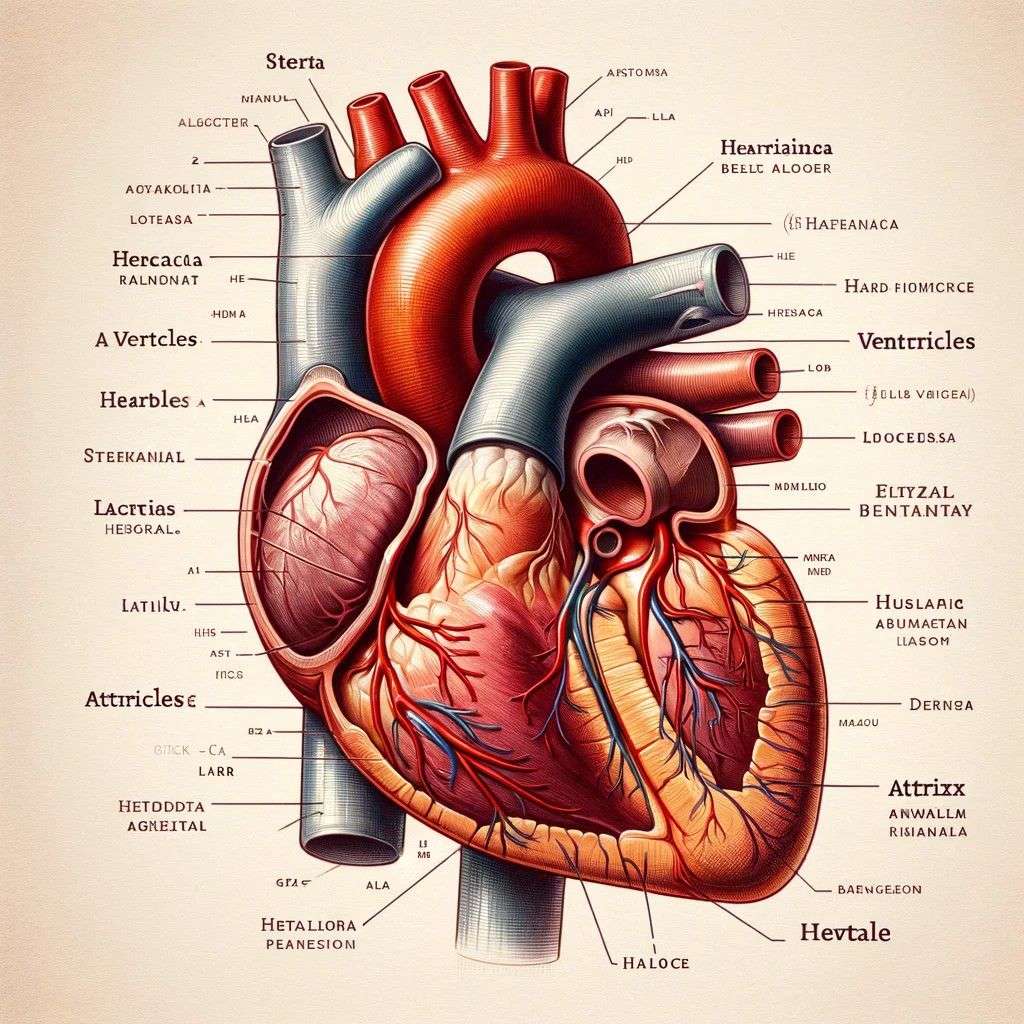
(Diagram)
- Auricles: Upper chambers that receive blood returning from the body (right) and lungs (left).
- Ventricles: Lower chambers that pump blood out of the heart. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs, while the left ventricle pumps blood to the rest of the body.
- Valves: Control the flow of blood between chambers and prevent backflow.
Function: The heart acts as a pump, circulating blood throughout the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients and remove waste products.
2. Types of Lenses:
- Convex Lenses: Thicker in the center than at the edges, converge light rays, and focus them to a point. Used for magnifying objects (magnifying glasses), correcting farsightedness (glasses), and focusing light in cameras and telescopes.
- Concave Lenses: Thinner in the center than at the edges, diverge light rays, and spread them out. Used for correcting nearsightedness (glasses) and wide-angle lenses in cameras.
3. Hydroelectric Power Plant:
- Water stored in a reservoir flows through a turbine, spinning its blades.
- The turbine rotation drives a generator, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- The electricity is then transmitted through power lines to homes and businesses.
4. Acids and Bases:
- Acids: Donate protons (H+) in aqueous solutions, have a sour taste, and change litmus paper red. Examples: lemon juice, vinegar, hydrochloric acid.
- Bases: Accept protons (H+) in aqueous solutions, have a bitter taste, and change litmus paper blue. Examples: baking soda, soap, ammonia.
5. Benefits and Risks of GMOs:
Benefits:
- Increased crop yields, leading to reduced food shortages.
- Resistance to pests and diseases, reducing pesticide use.
- Improved nutritional content of food.
Risks:
- Unforeseen environmental impacts, such as harm to beneficial insects or unintended spread of genetic traits.
- Potential allergens or toxins in genetically modified crops.
- Ethical concerns about altering organisms and potential for corporate control of food production.
6. Importance of Biodiversity:
- Provides habitat for various species, ensuring their survival and ecological balance.
- Supports nutrient cycles, returning essential elements to the ecosystem.
- Maintains healthy soil and water quality, crucial for plant growth and human well-being.
- Offers potential for new medicines and resources through the diverse range of organisms and their adaptations.
Section E: Long Answer (3 marks each, total 9 marks)
1. Photosynthesis:
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (sugar) and oxygen. It is the foundation of life on Earth as it provides energy for most living things.
Raw Materials:
- Sunlight: Energy source to drive the process.
- Water: Used as a reactant and provides hydrogen atoms for glucose synthesis.
- Carbon dioxide: Used as a reactant for building organic molecules like glucose.
Products:
- Glucose: The primary energy source for plants and other organisms.
- Oxygen: Released into the atmosphere, sustaining life for most organisms.
Steps of Photosynthesis:
- Light Capture: Chlorophyll pigments in leaves absorb sunlight energy.
- Electron Transport: Light energy excites electrons, leading to a chain of reactions that generate ATP (energy currency) and NADPH (electron carrier).
- Carbon Fixation: Carbon dioxide enters the Calvin Cycle, where it is combined with NADPH and ATP to form sugars like glucose.
- Regeneration: NADPH and ATP are regenerated for further cycles.
2. Human Nervous System:
The human nervous system is a complex network of nerves and specialized cells responsible for controlling all body functions, receiving and processing sensory information, and generating responses.
Structure:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain and spinal cord. The brain processes information and sends commands, while the spinal cord relays signals between the brain and body.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Sensory and motor nerves. Sensory nerves carry information from the senses to the CNS, while motor nerves carry commands from the CNS to the muscles and organs.
- Neurons: Basic units of the nervous system, transmitting electrical signals through axons and dendrites.
Function:
- Controls movement and muscle coordination.
- Processes sensory information like sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
- Regulates vital functions like heart rate, breathing, and digestion.
- Enables learning, memory, and emotions.
3. Newton’s Laws of Motion:
Sir Isaac Newton formulated three fundamental laws governing the motion of objects:
First Law: Law of Inertia – An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
Example: A car coasting on a flat road maintains its speed unless it encounters friction or brakes.
Second Law: Law of Acceleration – The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
Example: A heavier object requires more force to accelerate than a lighter one.
Third Law: Law of Action and Reaction – For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Example: When a rocket fires its engine, the hot gases pushing out (action) propel the rocket forward (reaction).
Section F: Essay Type (4 marks each, total 12 marks)
1. Impact of Human Activities on Climate Change and Mitigation Solutions:
Human activities significantly influence climate change:
- Burning fossil fuels: Releases greenhouse gases (GHGs) like carbon dioxide and methane, trapping heat in the atmosphere and causing global warming.
- Deforestation: Reduces the Earth’s capacity to absorb CO2, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
- Industrial processes: Generate GHGs and pollutants, further affecting climate patterns.
- Intensive agriculture: Contributes to methane emissions from livestock and releases nitrous oxide from fertilizers.
Consequences of climate change include:
- Rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
- More extreme weather events like heatwaves, droughts, floods, and storms.
- Disruptions in agricultural yields and food security.
- Loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services.
To mitigate climate change, we need:
- Transition to renewable energy sources: Solar, wind, geothermal, and hydro power can replace fossil fuels and reduce GHG emissions.
- Improve energy efficiency: Reduce energy consumption in homes, industries, and transportation.
- Protect and restore forests: Enhance carbon sequestration and promote sustainable land management.
- Invest in green technologies: Develop carbon capture and storage technologies and sustainable transportation solutions.
- Adopt climate-friendly practices: Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint through eco-friendly choices like using public transport, reducing waste, and consuming responsibly.
2. Importance of Renewable Energy Sources for a Sustainable Future:
Renewable energy sources are crucial for building a sustainable future due to several reasons:
- Environmental benefits: Reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, mitigating climate change and improving public health.
- Sustainability: Renewable resources are naturally replenished and minimize depletion of finite resources like fossil fuels.
- Energy security: Reduce dependence on volatile fossil fuel markets and geopolitical conflicts for energy needs.
- Economic growth: Create new jobs in renewable energy industries and stimulate technological innovation.
- Improved quality of life: Cleaner air and reduced environmental degradation lead to healthier communities and ecosystems.
Transitioning to renewable energy requires significant investments in infrastructure development, policy changes, and raising public awareness. However, the long-term benefits for environmental protection, economic development, and overall well-being make it a vital path for a sustainable future.
3. The Scientific Method and Developing New Knowledge:
The scientific method is a systematic approach to investigating the natural world and developing new knowledge and understanding. It involves:
- Observation: Identifying a phenomenon or problem based on data and evidence.
- Question formulation: Forming a specific question or hypothesis to be tested.
- Research and evidence gathering: Conducting experiments, collecting data, and reviewing existing research.
- Analysis and interpretation: Analyzing data and drawing conclusions based on the evidence.
- Validation and communication: Sharing findings through peer review, publications, and further research.
The scientific method provides a rigorous framework for ensuring the reliability and accuracy of new knowledge. It allows for questioning existing assumptions, testing hypotheses, and revising conclusions based on new evidence. This continuous process of inquiry fuels scientific progress and advances our understanding of the world around us.
.